US Wholesale Electricity Markets: MISO’s Energy Storage Imperative
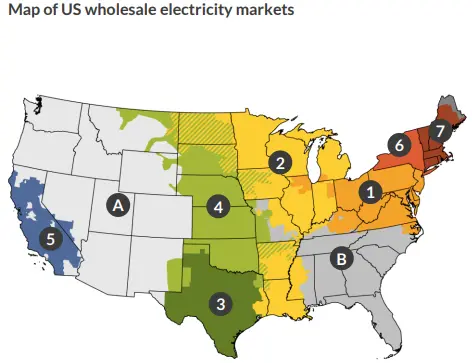
Map Overview
Image Source: ACP – Map of US wholesale electricity markets
MISO’s Energy Storage Surge Requirement
A report by the American Clean Power Association (ACP) and Aurora Energy Research reveals that the MISO service area will need a 500% increase in battery storage by 2035. ACP commissioned Aurora to conduct this study, highlighting a significant opportunity to enhance grid reliability and reduce energy system costs through large-scale energy storage deployment across MISO.
MISO’s Geographic and Operational Scope
MISO stands as the largest regional transmission organization (RTO) in the US, covering Arkansas, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kentucky, Louisiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Texas, Wisconsin, and the Canadian province of Manitoba. The RTO faces growing load demands that its aging energy generation resources cannot adequately meet.
Electricity Price Variability and Infrastructure Constraints
Due to MISO’s vast coverage and limited transmission infrastructure, electricity prices exhibit significant variation. This summer, MISO witnessed capacity prices surge over 2,000%. Without energy storage additions, modeling indicates that peak electricity prices for consumers will continue to rise and become less reliable.
Cost Implications of Inadequate Energy Storage
- Peak Price Projections: Without battery storage, peak electricity prices during high-demand hours could reach US$159 per MWh or higher by 2035.
- Legacy Infrastructure Costs: Greater reliance on outdated energy infrastructure could add US$493 million in electricity costs.
- Price Spikes: In a future without energy storage, daily electricity prices could spike nearly three times higher compared to a scenario with expanded energy storage capacity.
Current and Projected Battery Storage Capacity
Currently, 126.5MW of batteries operate in MISO, with Aurora’s report expecting 980MW to be online by next spring. The interconnection queue contains 351GW of capacity across all technologies, with over 25GW of batteries entering the queue in 2024. The total capacity entering the 2023 interconnection queue is 115GW, 31% lower than in 2022, attributed to queue reforms raising entry barriers.
Energy Storage’s Economic Benefits
Deploying over 10,000MW of energy storage from 2025 to 2035 will ensure reliable power for Midwestern and Central US states amid economic expansion and rising electricity demand. This could save the region more than US4.5billionby2035andgenerateoverUS25 billion in energy cost savings over the next two decades.
Key Policy Changes for Energy Storage Success
- Market Rule Updates: Electricity market rules must evolve to fairly value flexible energy storage resources.
- Interconnection Acceleration: Streamline the interconnection process to eliminate delays in connecting new energy storage resources to the grid.
- Permitting Streamlining: Clarify and streamline permitting at state and local levels for safe, responsible, and rapid infrastructure development.
- State Targets and Procurements: Advance state targets and procurements demonstrating commitment to new energy infrastructure, such as energy storage.
MISO’s Methodology Reforms
In April, ACP highlighted reforms US grid operators, including MISO, needed to implement based on findings from the Brattle Group. MISO must reform its Direct Loss of Load (DLOL) methodology and Loss of Load Expectation (LOLE) modeling. DLOL reforms should incorporate probabilistic analysis assessing resource performance during high-risk periods, while LOLE should better reflect weather variability, renewable energy sources, and demand changes.
Frequency Regulation Market Participation
According to the Great Plains Institute, batteries in MISO have historically generated more revenue in the frequency regulation market than the capacity market. This trend may persist until transmission infrastructure upgrades occur. In June, NERC’s 2025 State of Reliability report noted instances in Texas where batteries provided 100% of total capacity for frequency regulation services in 2024, demonstrating batteries’ role in restoring grid frequency and preventing load shed.
Keywords: MISO Energy Storage, US Wholesale Electricity Markets, Grid Reliability, Battery Storage Capacity, Electricity Price Variability, Energy Storage Policy, Frequency Regulation Market, Interconnection Queue Reforms