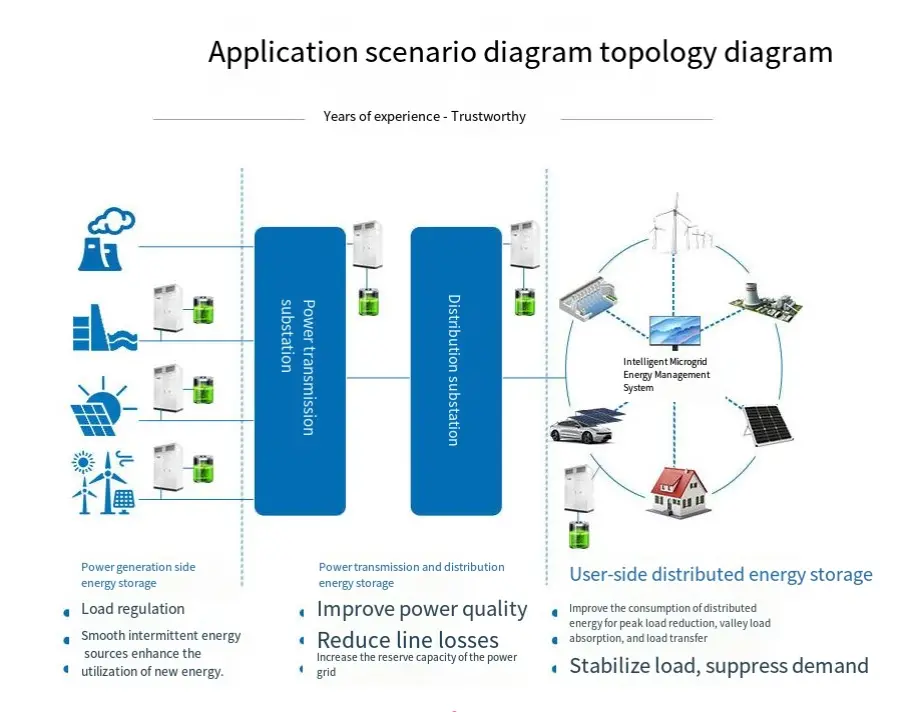
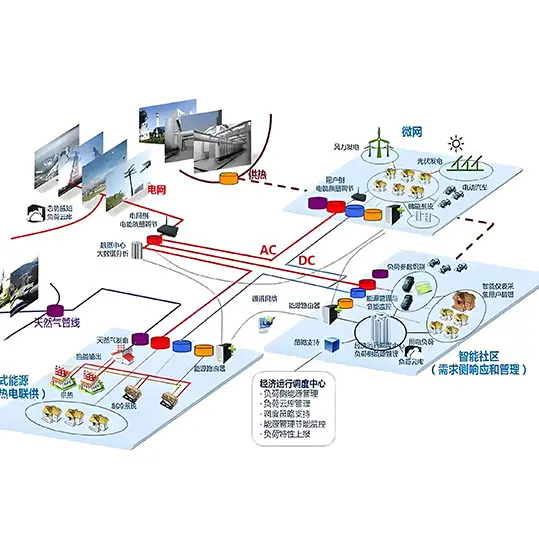
Industrial and Commercial Energy Storage Cabinets: A Game-Changer for Diverse Sectors
Energy storage cabinets, also recognized as Industrial and Commercial Energy Storage Systems (ESS), are gaining rapid integration across various industries. They store energy from renewable sources like solar and wind and release it during peak demand, optimizing energy utilization. Beyond cost reduction, they enhance sustainability, reliability, and grid stability. Here’s a detailed look at their applications across key sectors:
Key Industries and Sectors
Solar Energy (Photovoltaic)
Application: ESS store excess solar energy generated during the day for use at night or on cloudy days when generation is low or demand is high.
Significance: Businesses achieve greater energy independence, reduce grid reliance, and cut costs by avoiding peak electricity rates. It stabilizes energy supply and supports renewable energy transition.
Manufacturing and Industrial Facilities
Application: Industrial ESS store energy during off-peak hours, enabling factories to use stored energy during peak demand or grid unreliability.
Significance: They reduce energy costs, minimize downtime from power interruptions, and boost operational efficiency. Smoothing energy demand supports consistent production cycles and better energy planning.
Commercial Real Estate (Offices, Malls, Retail)
Application: ESS in commercial buildings store excess solar energy or reduce peak-hour electricity consumption. They also serve as backup power during outages.
Significance: Energy storage lowers electricity bills, ensures energy security, and enhances building sustainability. Critical systems (HVAC, lighting, security) stay operational during grid failures, vital for continuous businesses.
Data Centers
Application: Energy-intensive data centers use ESS to balance load and ensure server continuity during power fluctuations or outages.
Significance: ESS maintain data security, reduce data loss risk, and avoid costly downtime. They integrate renewable energy, enabling sustainable operations and lower energy costs.
Telecommunications
Application: Telecom towers and equipment rely on ESS for uninterrupted power, especially in remote or off-grid locations with unstable energy access.
Significance: Energy storage ensures uninterrupted telecom operations, even in unreliable grid regions. It supports solar and wind integration, reducing diesel generator reliance and making operations eco-friendlier.
Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Stations
Application: ESS at EV charging stations store renewable energy, making charging more sustainable. They balance demand during peak hours and optimize charging speeds.
Significance: This improves charging infrastructure reliability, allows clean energy use, reduces EV environmental footprint, and ensures smooth operations during high demand.
Agriculture
Application: In agriculture, ESS store solar or wind energy to power irrigation systems, farm equipment, or storage facilities.
Significance: Farmers lower energy costs, reduce fossil fuel dependence, and enhance operation resilience against outages or fluctuating energy prices.
Overall Significance of Industrial and Commercial ESS
Cost Savings
Businesses store energy during off-peak hours and use it during peak demand, avoiding high electricity rates and reducing bills.
Grid Independence
ESS help industries achieve energy self-sufficiency, minimizing grid failure, price fluctuation, and external supplier dependence impacts.
Sustainability
Integrating renewable energy sources like solar or wind reduces carbon footprint, contributes to sustainability goals, and meets environmental regulations. ESS enhance renewable energy efficiency, paving the way for a cleaner future.
Reliability and Backup Power
ESS serve as crucial backup power during outages, ensuring business continuity in critical industries like healthcare, telecom, and data management.
Energy Efficiency
Energy storage shifts consumption from peak to off-peak hours, improving energy system efficiency and reducing waste.
Grid Support and Load Management
In unstable grid regions or power shortage areas, ESS stabilize the grid by absorbing excess energy during low demand and releasing it during high demand, smoothing fluctuations and enhancing reliability.
Enhanced Energy Management
ESS enable sophisticated energy management systems, allowing businesses to track consumption and optimize usage based on real-time data. This capability aids better demand forecasting and planning.
Conclusion
Industrial and commercial energy storage cabinets are vital for sectors aiming to optimize energy use, reduce costs, and enhance sustainability. Whether integrating renewable energy, ensuring backup power, or achieving energy independence, ESS plays a pivotal role in transforming business energy management and consumption.
Keywords: Industrial Energy Storage, Commercial Energy Storage Systems, Renewable Energy Integration, Energy Cost Reduction, Grid Stability