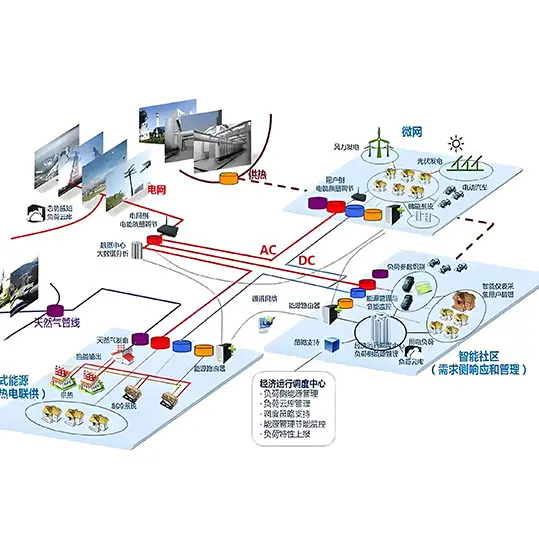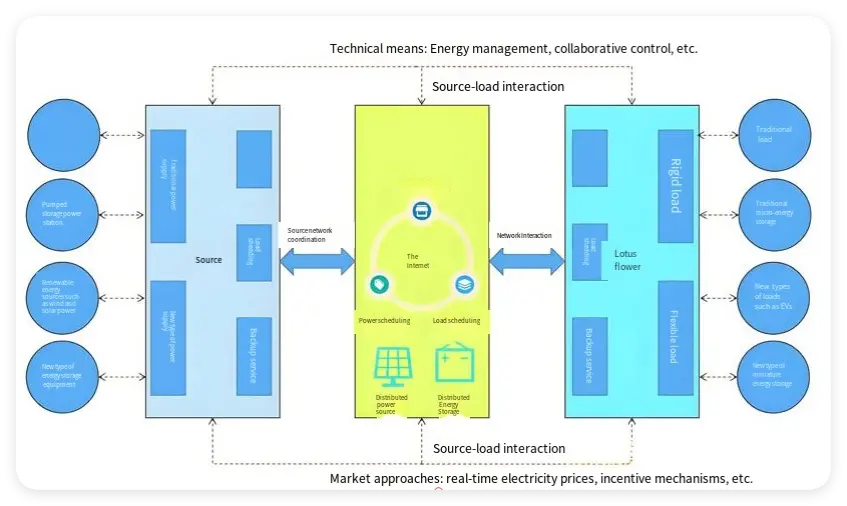
Comprehensive Analysis of Energy Classification and Its Application Scenarios
In the current era of energy transition and the push for efficient utilization, having a precise understanding of different energy source classifications and their application scenarios is of utmost importance. Here’s a detailed look at the four major categories: energy production, power grid management, power demand, and energy storage systems, along with their sub – categories and application scenarios.
Source (Energy Production)
Energy production serves as the foundation of the energy supply chain, providing essential energy support for society as a whole.
Photovoltaic Power Generation
There are two main forms: distributed and centralized photovoltaic power generation. Distributed photovoltaic power generation is typically installed on the rooftops of residential, commercial buildings, and industrial parks. It generates and consumes electricity locally, effectively reducing transmission losses. Centralized photovoltaic power generation involves building large – scale photovoltaic power stations, suitable for areas with high power demand, such as providing centralized power supply for industrial parks.
Wind Power Generation
It can be divided into offshore and onshore wind power. Offshore wind power harnesses the rich wind resources at sea. It is suitable for large – scale grid connection, offering clean energy to coastal areas and being a significant part of green energy projects. Onshore wind power is set up in areas with abundant wind resources on land and finds wide application in green energy projects.
Biomass Power Generation
Through biomass cogeneration technology, agricultural waste and urban garbage are converted into electrical and thermal energy. This approach not only addresses the waste disposal issue but also enables energy recovery. It plays a vital role in agricultural production areas and urban energy supply.
Hydropower Generation
Conventional hydropower and pumped – storage power stations are the main types. Conventional hydropower converts the kinetic energy of flowing water into electrical energy. It is suitable for large – scale hydropower projects, providing stable power output to the national grid. Pumped – storage power stations play a crucial role in grid frequency modulation and dispatching. They store energy during periods of low power demand and generate electricity during peak – demand periods to balance the grid load.
Hydrogen Production
Hydrogen is produced based on renewable energy. The produced hydrogen is used as a raw material or fuel in industrial production and in energy storage systems. This facilitates energy storage and regulation, promoting the efficient utilization of renewable energy.
Grid (Power Grid Management)
Power grid management ensures the safe and stable transmission of electricity from the production end to the demand end.
Smart Grid
Smart grids achieve automation, remote monitoring, and load optimization of power systems. In urban power grids, industrial parks, and large – scale infrastructure, smart grids can sense power supply and demand in real – time. They automatically adjust power distribution, enhancing power supply reliability and efficiency.
Microgrid
As a small – scale local grid, microgrids are suitable for remote areas, island power supply, and emergency backup power systems. In remote areas, microgrids can operate independently to meet the power needs of local residents and businesses. During emergencies, they act as backup power sources to ensure the normal operation of critical facilities.
Power Grid Dispatching – Centralized Dispatching System
For large – scale power grids and power companies, the centralized dispatching system conducts real – time monitoring and adjustment of power systems. This system allows for timely understanding of the power grid’s operation status and reasonable allocation of power resources to ensure stable grid operation.
High – Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Transmission
HVDC transmission is ideal for long – distance and large – capacity power transmission, especially when connecting offshore wind power to on – shore power grids. This technology effectively reduces energy losses during transmission and improves transmission efficiency.
Load (Power Demand)
Power demand – side management is crucial for optimizing energy allocation and improving energy utilization efficiency.
Demand Response
Demand response adjusts power supply according to changes in power demand. It is applied in residential, commercial, and industrial demand management, particularly for optimizing load distribution during peak periods. Through price signals or incentive measures, users are encouraged to reduce power consumption during peak hours and increase it during off – peak hours, enabling rational use of power resources.
Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Network
Smart charging stations and the electric vehicle network form the charging infrastructure, suitable for the transportation sector and fast – charging facilities for electric vehicles. With the growing popularity of electric vehicles, the construction and improvement of the charging network are essential for ensuring their usage.
Smart Building Management
Smart building management integrates power management within buildings and optimizes power consumption structures. It is widely used in large – scale commercial buildings, office buildings, and residential quarters. Through intelligent control systems, precise control of lighting, air – conditioning, elevators, and other equipment is achieved, reducing energy consumption.
Data Center
Data centers are important application scenarios for efficient power use and cooling systems. They require a stable and reliable power supply and efficient cooling technologies to ensure the normal operation of information technology companies and stable energy supply.
Storage (Energy Storage Systems)
Energy storage systems play a key role in energy storage and regulation.
Battery Energy Storage System (BESS)
Large – scale energy storage batteries are used for power balance and peak – shaving. They are widely applied in power grid dispatching and renewable energy power stations. These batteries store electrical energy when there is a surplus and release it when there is a shortage, improving grid stability and the absorption capacity of renewable energy.
Pumped Hydro Storage
This method stores energy by lifting and lowering water. It is suitable for grid load regulation and supplementing renewable energy fluctuations. During low – load periods, excess electrical energy is used to pump water to a high – altitude reservoir. During peak – load periods, water is released to generate electricity, realizing spatial – temporal energy transfer.
Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES)
Compressed air is stored in underground cavities, suitable for large – scale energy storage and power balance. It offers advantages such as large energy storage capacity and long energy storage cycle, effectively addressing the intermittency issue of renewable energy.
Hydrogen Energy Storage
Hydrogen energy storage adopts hydrogen storage technology, suitable for long – cycle storage, cross – season storage, and long – term energy reserves. Hydrogen is easy to store and transport, enabling large – scale and long – term energy storage.
Flywheel Energy Storage
It is used for short – term high – power demand, suitable for frequency regulation and fast response of power balance. Flywheel energy storage has the benefits of fast response and multiple charge – discharge cycles, playing an important role in the rapid regulation of power systems.
Supercapacitor Energy Storage
Supercapacitor energy storage is used for fast charge – discharge, suitable for electric vehicles, rail transit systems, and grid stability. Supercapacitors feature high power density and fast charge – discharge, meeting instantaneous high – power demands.
Understanding the classification of energy and its application scenarios helps us better plan energy development strategies and promote efficient utilization and sustainable development of energy. With the continuous progress of technology, the application scenarios of various energy sources will continue to expand and optimize.